Speech Therapy
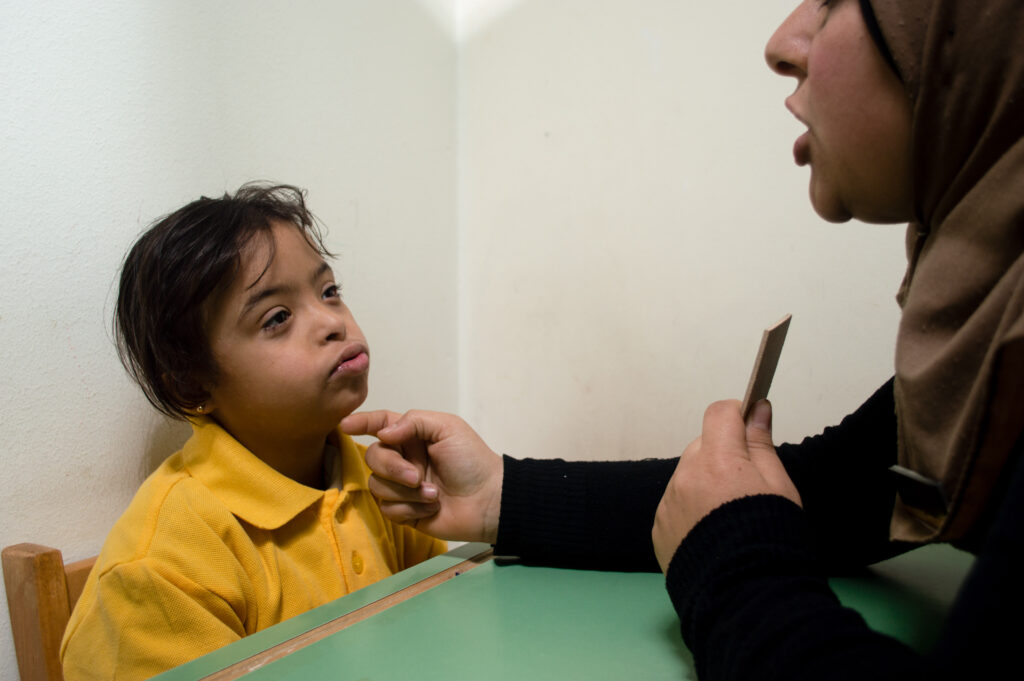
Speech therapy, also known as speech-language therapy or speech-language pathology, is a clinical intervention that aims to assess, diagnose, treat, and prevent speech, language, communication, and swallowing disorders in individuals of all ages. Speech-language pathologists (SLPs), also known as speech therapists, provide this therapy. Here’s a comprehensive overview of speech therapy:
Key Concepts of Speech Therapy
1. Speech Disorders:
- Articulation Disorders: Difficulty in producing sounds correctly.
- Fluency Disorders: Problems such as stuttering, affecting the flow of speech.
- Voice Disorders: Issues with pitch, volume, or quality of voice.
2. Language Disorders:
- Receptive Language Disorders: Difficulty in understanding or processing language.
- Expressive Language Disorders: Difficulty in expressing thoughts and ideas.
- Pragmatic Language Disorders: Problems with the social use of language.
3. Communication Disorders:
- Aphasia: Loss of ability to understand or express speech, typically due to brain injury.
- Social Communication Disorders: Difficulties with the social aspects of verbal and nonverbal communication.
4. Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia):
- Oral Dysphagia: Issues with the mouth phase of swallowing.
- Pharyngeal Dysphagia: Problems in the throat phase of swallowing.
- Esophageal Dysphagia: Difficulties in the esophageal phase of swallowing.
Goals of Speech Therapy
- Improve Articulation:.
- Enhance Language Skills:
- Improve Fluency:
- Strengthen Voice Quality:
- Enhance Social Communication:
- Improve Swallowing Function:
Techniques and Methods in Speech Therapy
1. Articulation Therapy:
- Purpose: To correct speech sound errors.
- Methods: Practicing specific sounds in isolation, syllables, words, and sentences.
2. Language Intervention Activities:
- Purpose: To improve language skills.
- Methods: Interactive activities like playing, talking, reading books, and using pictures to stimulate language development.
3. Fluency Therapy:
- Purpose: To reduce stuttering.
- Methods: Techniques such as easy onset, light articulatory contact, and controlled breathing.
4. Voice Therapy:
- Purpose: To improve vocal quality and health.
- Methods: Vocal hygiene education, pitch and volume exercises, and resonance therapy.
5. Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC):
- Purpose: To support communication for individuals with severe speech or language impairments.
- Methods: Using communication boards, speech-generating devices, and sign language.
6. Swallowing Therapy:
- Purpose: To improve swallowing safety and efficiency.
- Methods: Exercises to strengthen muscles involved in swallowing, techniques to improve coordination, and dietary modifications.
Conditions Treated with Speech Therapy
- Developmental Delays: Speech and language delays in children.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Communication difficulties associated with autism.
- Aphasia: Language impairments due to stroke or brain injury.
- Cerebral Palsy: Motor speech disorders.
- Voice Disorders: Such as vocal nodules or polyps.
- Dysarthria: Motor speech disorders resulting from neurological conditions.
- Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia): Resulting from various medical conditions.
Benefits of Speech Therapy
- Improved Communication Skills: Enhances the ability to express thoughts and understand others.
- Greater Independence: Facilitates participation in social, educational, and vocational activities.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Reduces frustration and improves social interactions.
- Safety in Swallowing: Ensures safe eating and drinking, reducing the risk of aspiration.
- Academic and Professional Success: Supports academic achievement and professional communication.
Example Speech Therapy Program
1. Initial Assessment:
- Purpose: To identify specific speech, language, or swallowing issues.
- Method: Comprehensive evaluation including case history, standardized tests, and observational assessments.
2. Goal Setting:
- Purpose: To establish individualized therapy goals.
- Method: Collaborating with the patient and family to determine realistic and functional goals.
3. Therapy Sessions:
- Purpose: To implement targeted interventions.
- Method: Regular sessions (weekly or biweekly) focusing on specific goals, using tailored activities and exercises.
4. Home Practice and Carryover:
- Purpose: To reinforce therapy goals outside of sessions.
- Method: Providing home practice materials and strategies for integrating skills into daily routines.
5. Progress Monitoring and Adjustments:
- Purpose: To track improvement and adjust therapy as needed.
- Method: Regular re-evaluations and progress reports, adjusting goals and techniques based on patient progress.
